
Effective project management is vital for the success of any organization. The ability to plan, execute, and deliver projects on time and within budget is critical for small businesses to large corporations. Even for seasoned professionals, navigating the complexities of project management can be a daunting task.
This article delves into the 6 most frequently asked project management questions, shedding light on common challenges and providing practical insights to improve project success. We draw from the collective wisdom of experienced project managers and industry best practices. Understanding these fundamental questions can provide invaluable guidance for your projects, whether you’re an aspiring project manager, a team member working on a project, or a business owner looking to streamline operations.
The Most Frequently Asked Project Management Questions
By addressing these common queries, we aim to demystify project management and equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to tackle your projects with confidence. So, if you’ve ever wondered, “What is the role of a project manager?” or “How can I effectively manage project risks?” then this article is for you.
1. What Is Project Management?
Project management is a discipline and set of practices that entails planning, organizing, and controlling resources and activities in order to achieve specific goals within a specified scope, budget, and timeframe. It is a methodical approach to initiating, planning, executing, monitoring, and closing projects in order to achieve desired results.

In a nutshell, project management entails coordinating various elements, such as people, tasks, timelines, and resources, in order to complete a project successfully. It includes defining project objectives, developing a project plan, allocating resources, managing risks, communicating with stakeholders, and monitoring progress.
Project management is useful in a wide range of industries and sectors, from construction to information technology to marketing and healthcare. It provides a structured framework for managing projects of varying sizes and complexities, ensuring their efficient and successful completion.
Organizations can optimize resources, reduce risks, improve collaboration, and ultimately deliver projects that meet the expectations of stakeholders by employing project management principles and methodologies. It provides a systematic approach to project execution, allowing teams to achieve their objectives while maintaining control over the scope, budget, and timeline of the project.
2. What Is the Role of a Project Manager?
The role of a project manager in project management is multi-faceted and crucial for the success of any project. Project managers serve as the central point of coordination, overseeing all aspects of a project from initiation to completion. Their primary objective is to ensure that the project is delivered on time, within budget, and with the desired quality.
Here are some key responsibilities and roles of a project manager:
Planning:
Project managers play a pivotal role in project planning. They define project goals, scope, and deliverables, and create a comprehensive project plan that outlines the tasks, timelines, and resources required for successful project execution. This involves breaking down the project into manageable phases and setting realistic objectives.
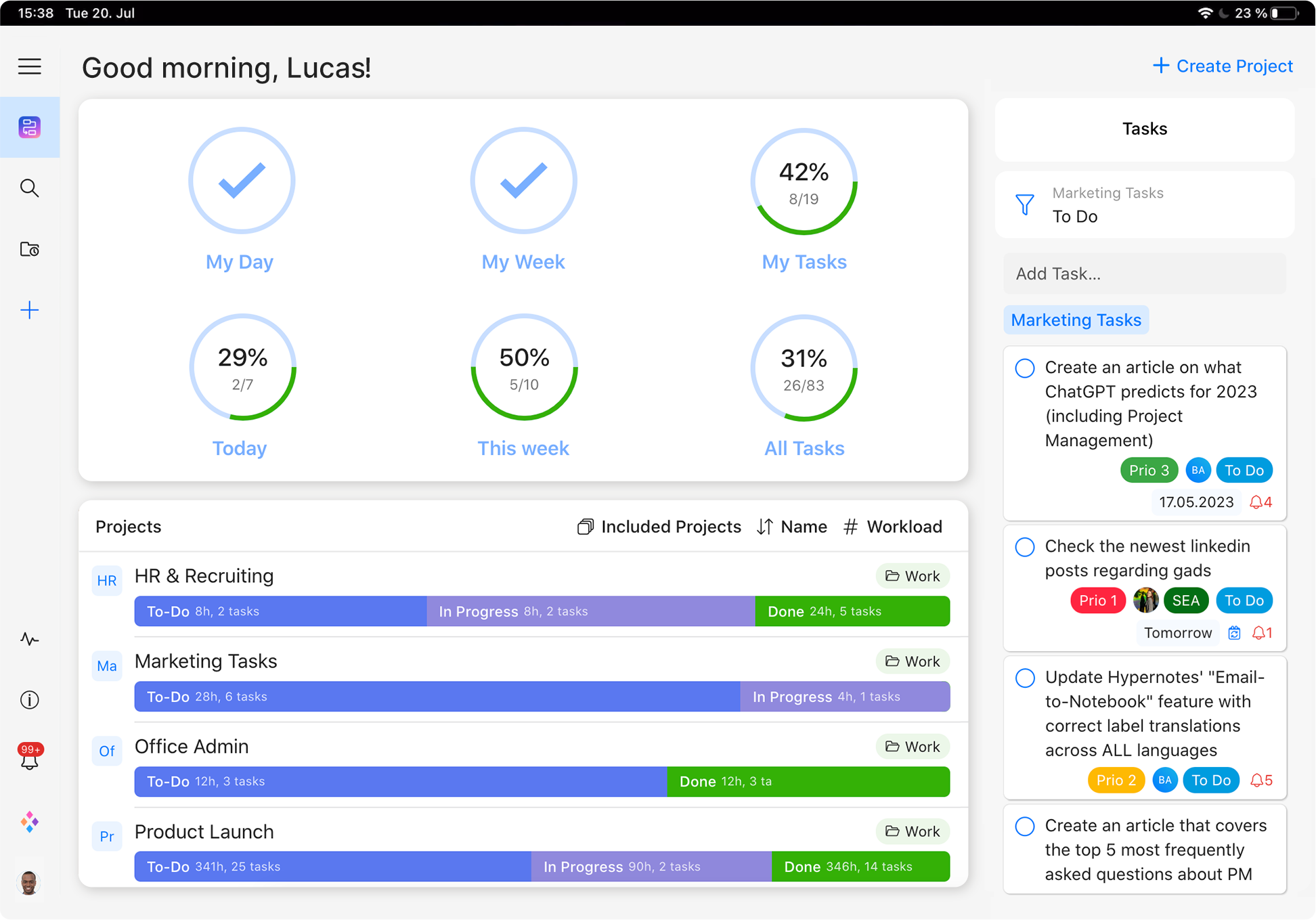
Discover the ultimate project management tool.
Sign up for free today!
Organizing and Resource Management:
Project managers coordinate resources, including human resources, equipment, materials, and finances. They allocate tasks to team members, ensure that resources are available when needed, and optimize their utilization to maximize efficiency.
Leadership and Team Management:
Project managers lead and motivate project teams, fostering a collaborative and productive work environment. They assign roles and responsibilities, provide guidance, and facilitate effective communication among team members. They also monitor team performance, address conflicts, and ensure that everyone is working towards common project goals.
Risk Management:
Project managers identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate or minimize their impact on the project. They conduct risk assessments, create contingency plans, and monitor risks throughout the project lifecycle. This proactive approach helps in anticipating and addressing challenges, ensuring project success.
Monitoring and Control:
Project managers continuously monitor project progress, track milestones, and compare actual progress against the project plan. They identify deviations, analyze their causes, and take corrective actions to keep the project on track. Regular status updates and reporting to stakeholders are also part of their responsibility.
Stakeholder Management:
Project managers engage with project stakeholders, including clients, team members, sponsors, and external parties. They ensure effective communication, manage expectations, and address stakeholder concerns. Building and maintaining positive relationships with stakeholders are crucial for project success.
Quality Assurance:
Project managers are responsible for ensuring that project deliverables meet the required quality standards. They define quality parameters, establish quality control processes, and conduct regular reviews to verify adherence to quality requirements.

Project managers are therefore accountable for driving projects towards successful outcomes by effectively planning, organizing, leading, and controlling project activities. Their role encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, requiring strong leadership, communication, and problem-solving skills to navigate the complexities of project management and achieve project objectives.
3. What Are the 5 Stages of Project Management?
The 5 stages of project management, commonly known as the project life cycle, provide a structured framework for managing projects from initiation to completion. While the specific terminology and processes may vary depending on the methodology used, the core stages typically include:
1st Stage: Project Initiation
- Define the project’s objectives, scope, and stakeholders.
- Conduct a feasibility study to assess the project’s viability.
- Develop a project charter or initiation document that outlines the project’s high-level details.
2nd Stage: Project Planning
- Create a detailed project plan that includes tasks, milestones, timelines, and resource requirements.
- Identify project dependencies, risks, and constraints.
- Develop a communication plan and stakeholder engagement strategy.
- Set project baselines for scope, schedule, and budget.
3rd Stage: Project Execution
- Execute the project plan by assigning tasks to team members and allocating resources.
- Manage and coordinate project activities, ensuring they are performed according to the defined schedule.
- Monitor progress and track project milestones.
- Manage changes and make necessary adjustments to keep the project on track.
4th Stage: Project Monitoring and Control
- Continuously monitor project performance against the baselines.
- Track and analyze project metrics, such as cost, schedule, and quality.
- Identify and manage risks and issues that may arise during project execution.
- Take corrective actions when deviations occur, and communicate updates to stakeholders.
5th Stage: Project Closure
- Validate project deliverables against acceptance criteria.
- Conduct a formal project review to assess project success and lessons learned.
- Close financial accounts, finalize contracts, and complete administrative tasks.
- Prepare a final project report and formally close the project.

It’s important to note that these stages are not always strictly linear, and iterations or overlapping activities may occur depending on the project’s nature and methodology used. Nonetheless, the five stages provide a general framework that helps project managers and teams navigate the project life cycle, ensuring a systematic and organized approach to project management.
4. How to Effectively Manage Project Risks
Effectively managing project risks is crucial for ensuring project success and minimizing the negative impact of unforeseen events. Here are some steps to help you manage project risks effectively:
Identify Risks:
Begin by identifying potential risks that could impact your project. This involves brainstorming with your project team, stakeholders, and subject matter experts to identify all possible risks. Consider risks related to project scope, resources, timeline, technology, external factors, and any other relevant aspects. Document these risks in a risk register or risk log.
Assess Risks:
Once risks are identified, assess their likelihood of occurring and their potential impact on the project’s objectives. Prioritize the risks based on their significance, using qualitative or quantitative assessment techniques. This will help you determine which risks require immediate attention and which ones can be managed or mitigated.
Plan Risk Response:
Develop a risk response plan for each identified risk. This plan outlines specific actions to address and mitigate the risks. Consider various strategies such as avoidance (eliminating the risk), mitigation (reducing the likelihood or impact), transfer (shifting the risk to another party), or acceptance (acknowledging the risk and having a contingency plan in place). Assign responsibilities and allocate resources for implementing the risk response strategies.
Monitor and Control:
Continuously monitor the identified risks throughout the project lifecycle. Regularly review and update the risk register to capture any new risks that may arise. Track the effectiveness of implemented risk response strategies and adjust as necessary. Maintain open communication channels to ensure that the project team remains aware of potential risks and can respond promptly.
Establish Contingency Plans:
Develop contingency plans for high-priority risks that pose a significant impact on the project if they occur. Contingency plans outline specific actions to be taken if a risk materializes. Having predetermined alternative approaches or backup plans can help minimize the impact of unforeseen events and ensure the continuity of project progress.
Engage Stakeholders:
Involve relevant stakeholders in the risk management process. Keep them informed about identified risks, mitigation strategies, and progress. Seek their input and support in addressing risks and obtaining necessary resources. Effective stakeholder engagement can help build a collaborative environment and enhance risk management effectiveness.
Learn from Lessons:
Continuously learn from past projects and experiences. Capture lessons learned from risk management efforts and incorporate them into future projects. This helps improve risk identification, assessment, and response planning for subsequent projects.

Remember that risk management is an ongoing process, and risks may evolve and change throughout the project lifecycle. Regularly revisit and update your risk management strategies to ensure they remain relevant and effective. By proactively identifying, assessing, and managing project risks, you can minimize potential disruptions and increase the likelihood of project success.
5. What Are the Key Project Management Skills?
Effective project management requires a combination of technical, interpersonal, and leadership skills. Here are some key project management skills that are essential for successful project execution:
Communication:
Strong communication skills are crucial for project managers to effectively convey information, expectations, and instructions to team members, stakeholders, and clients. Clear and concise communication helps ensure everyone is on the same page, promotes collaboration, and minimizes misunderstandings.
Leadership:
Project managers need to provide strong leadership to guide their teams towards project success. This includes inspiring and motivating team members, setting clear goals and expectations, making decisions, and resolving conflicts. Effective leadership encourages teamwork, fosters a positive work environment, and keeps the project on track.
Organization and Time Management:
Project managers must possess excellent organizational and time management skills to handle multiple tasks, meet deadlines, and manage resources efficiently. Being able to prioritize activities, create realistic schedules, and effectively allocate resources helps maintain project progress and prevent delays.
Risk Management:
The ability to identify, assess, and mitigate risks is crucial for project managers. They should be skilled in anticipating potential risks, analyzing their impact, and developing appropriate strategies to minimize or address them. Proactive risk management helps reduce the negative impact of unforeseen events on the project.
Problem-Solving:
Project managers encounter challenges and obstacles throughout the project lifecycle. Strong problem-solving skills enable them to identify issues, analyze root causes, and develop creative solutions. The ability to think critically and make timely decisions helps keep the project moving forward and overcome roadblocks.
Stakeholder Management:
Project managers need to effectively engage and manage various stakeholders, including clients, team members, sponsors, and external parties. Building and maintaining positive relationships, understanding stakeholders’ needs and expectations, and managing communication channels are vital for stakeholder satisfaction and project success.
Adaptability:
Projects are subject to changes and uncertainties. Project managers should be adaptable and flexible in response to evolving circumstances. They need to be open to change, adjust project plans as necessary, and find alternative approaches when required. Adapting to unexpected situations helps maintain project momentum and deliver successful outcomes.
Financial and Budget Management:
Understanding project finances and effectively managing budgets is essential for project managers. They should have a good grasp of financial concepts, be able to track and control project costs and make informed decisions to optimize resource allocation.
Team Management:
Project managers are responsible for leading and managing project teams. This requires strong team management skills, including the ability to delegate tasks, provide guidance and support, foster collaboration, and recognize and leverage individual strengths.
Continuous Learning:
Project managers should have a mindset of continuous learning and improvement. Keeping up with industry trends, best practices, and emerging project management methodologies helps enhance their skills and adapt to evolving project management practices.

While this list provides a comprehensive overview, the specific skills required may vary depending on the project’s nature, industry, and organizational context. Developing and refining these skills can significantly enhance a project manager’s ability to navigate complex projects and deliver successful outcomes.
6. What Are Project Management Tools?
Project management tools are software applications or platforms that assist project managers and teams in planning, organizing, tracking, and collaborating on projects. These tools help streamline project management processes, improve communication, and enhance overall project efficiency.
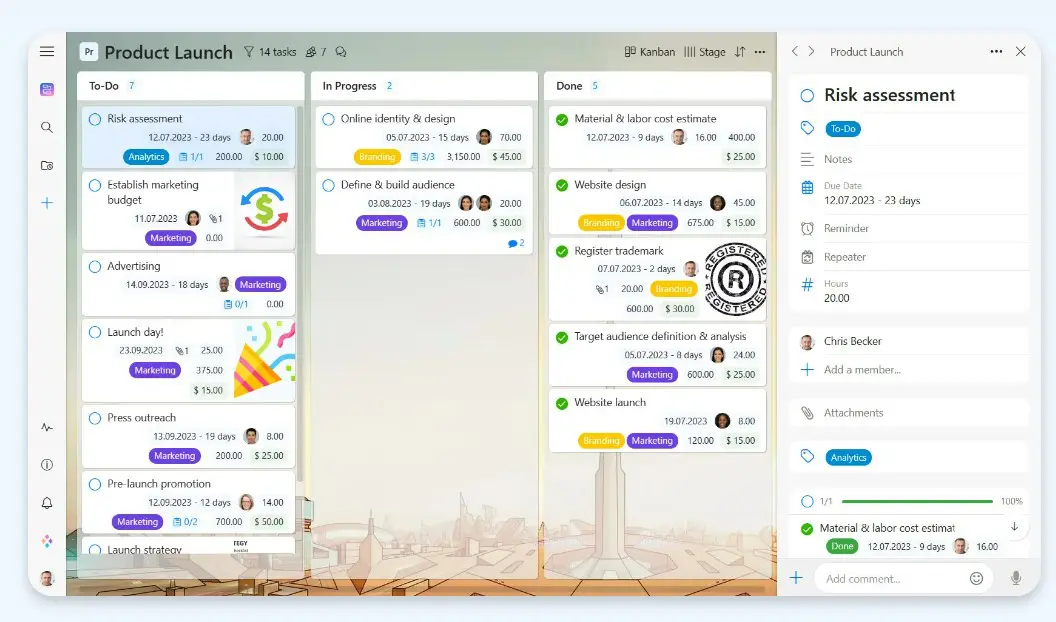
Here are some commonly used project management tools:
Project Planning and Scheduling Tools:
- Gantt Chart Tools: These tools, such as Microsoft Project or Zenkit allow project managers to create visual timelines, assign tasks, set dependencies, and track progress using Gantt charts.
- Kanban Boards: Tools like Jira or Zenkit enable teams to manage and visualize tasks using a Kanban board layout, with cards representing individual tasks or work items.
Collaboration and Communication Tools:
- Communication Platforms: Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Zenchat facilitate real-time communication and collaboration among team members, allowing for efficient sharing of information, discussions, and file sharing.
- Document Sharing and Collaboration Tools: Platforms such as Google Drive, SharePoint, or Dropbox provide a central location for teams to store, access, and collaborate on project-related documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.
Task and Workflow Management Tools:
- To-Do Lists and Task Managers: Tools like Any.do or Zenkit To Do help individuals and teams create and manage to-do lists, set deadlines, and track progress on tasks.
- Workflow Automation Tools: Platforms like Zapier or IFTTT automate repetitive tasks by integrating various applications and triggering actions based on predefined rules.
Time and Resource Management Tools:
- Time Tracking Software: Tools such as Toggl, Harvest, or Clockify help track time spent on project tasks, providing insights into resource utilization, estimating project costs, and analyzing productivity.
- Resource Planning Tools: These tools, such as ResourceGuru, Float, Teamdeck, or Zenkit assist in scheduling and allocating resources, managing team availability, and avoiding over/underbooking of resources.
Issue and Risk Management Tools:
- Issue Tracking Systems: Tools like Jira, GitHub Issues, or Redmine allow project teams to report, track, and manage project issues, bugs, and feature requests, ensuring they are addressed and resolved efficiently.
- Risk Management Software: Platforms such as RiskyProject, ProjectManager.com, or ActiveCollab provide features to identify, assess, track, and mitigate project risks, helping project managers proactively manage potential threats.
Reporting and Analytics Tools:
- Dashboard and Reporting Tools: Platforms like Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, or Google Data Studio help project managers visualize and present project data in the form of interactive dashboards and reports, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
- Project Performance Analytics: Tools such as ProjectManager.com, Workfront, or Smartsheet offer built-in analytics capabilities to track project progress, monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), and generate performance reports.
The selection of project management tools depends on the specific needs and requirements of the project, team size, budget, and preferences. It’s important to evaluate different tools and choose those that align with the project management approach, team collaboration needs, and overall project goals.
Final Thoughts
Project management is certainly a complex and multifaceted discipline that requires a diverse set of skills and knowledge. Hopefully, this article has provided valuable insights into the 6 most frequently asked project management questions. By understanding these key discussion points, individuals can navigate the challenges of project management more effectively and increase the chances of project success.
Whether you are an aspiring project manager or a seasoned professional, having a solid foundation in project management concepts and best practices is essential. By familiarizing yourself with the fundamental principles and applying them in your projects, you can improve your ability to plan, execute, and control projects, leading to better outcomes and stakeholder satisfaction. Additionally, staying updated with the latest trends, methodologies, and tools in project management can help you adapt to the evolving needs of the industry and continuously improve your project management skills.




Leave a Reply