10 Most Popular Project Management Methodologies: An Overview
Find the right approach for you and your team!

Choosing the right project management framework is the foundation of every successful project. Project managers have a broad portfolio of proven and modern project management methodologies at their disposal. In particular, agile project management methods like Scrum and Kanban have now become absolute trend strategies.
But be careful: One-for-All does not apply in project management! Each project has individual characteristics, requirements, and risks that you should definitely consider when choosing the appropriate project management method.
In this article, we present the 10 most renowned project management solutions and show you exactly what is suitable for you and your company.
The following points will be covered in this article:
✅ Important principles for selecting your project management framework
✅ The 10 most effective project management methodologies and their key characteristics
✅ Examples for choosing the most suitable approach for your team
Project Management Methodologies: More structure and less risk
Projects aim to achieve a specific, unique goal, such as the development of new software. This must be accomplished within a certain timeframe without exceeding the predefined limits of personnel, monetary, and time resources. If project managers approach this task unprepared and disorganized, it is very likely that the project will fail.
The more complex the project, the higher the external risk factors, and the more employees involved, the more important it is to approach the project in a structured and systematic manner.
Finding “The One”
A project management methodology that represents an universal solution for all project types seems desirable. However, we must quickly abandon this thought. Projects are defined by their unique nature. They differ significantly in the following factors:
- Strategic goal alignment and company values
- Key business factors (e.g., pricing strategies)
- Stakeholder requirements
- Project risks
- Project size
- Resource availability
- Project complexity
- Time frame
What works for one project can be completely unsuitable for another. These individual differences require tailored approaches in project management. A one-size-fits-all solution is not capable of meeting the specific requirements and challenges of each project.
Project Management Methodologies in comparison
Agile? Lean? Waterfall? Project managers are spoilt for choice. The following project management methodologies have already established themselves in practice. Now it’s time to decide which method fits your principles and processes.
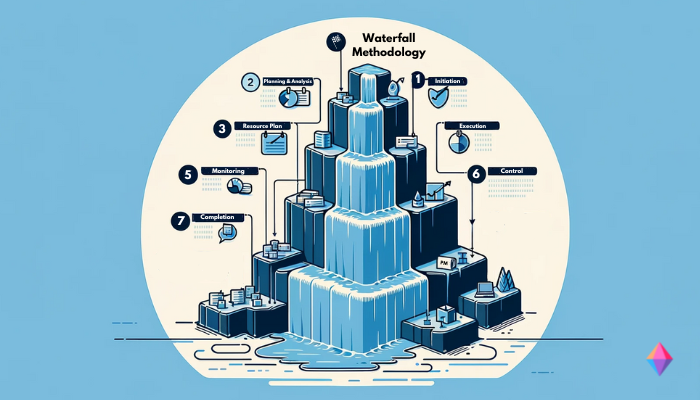
1. Waterfall Methodology
The Waterfall methodology is a traditional project management method. It proceeds step by step – like a waterfall – in these phases:
- Initiation
- Planning and Analysis
- Setting up the Resource Plan
- Execution
- Monitoring
- Control
- Completion of the Project
All tasks of the project are processed according to the fixed sequence of the Waterfall project management methodology. New tasks are only started when the previous ones are completed.
In the framework of the Waterfall method, the project manager plans in advance exactly the required resource deployment and aligns the entire planning of the project management process accordingly. Unlike agile project management methodologies, no feedback processes are provided within the individual project steps. The Waterfall methodology allows only minimal deviation from the pre-established resource planning.
What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
The Waterfall methodology is particularly suitable for projects whose tasks are dependent on each other. Projects that follow this method shouldn’t be very extensive and of short duration. Or they should include tasks that are repetitive and already known to the participants. The Waterfall methodology is well suited, for example, for projects in production that primarily involve sequential processes. These sequential phases and processes are often visualized in Waterfall project management using Gantt charts.
In the implementation of step-by-step project management frameworks, errors often become apparent only at the end of a project. Therefore, the Waterfall methodology is not well suited for projects with many unpredictable factors.
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| Clear Structure and Phases | Rigidity and Lack of Flexibility |
| Simple Administration and Planning | Late Delivery and Feedback |
| Early Identification of Requirements | High Risk in Uncertainty and Complexity |
Unknown Fact: Although the Waterfall methodology is often seen as traditional and sequential, it did not originate in computer science or engineering. In fact, the Waterfall methodology was first introduced in an article by Dr. Winston W. Royce in 1970, where he described the project management method as problematic and prone to errors. Ironically, the Waterfall methodology still became popular. Today it’s one of the most well-known project management methodologies, even though its original creator viewed its application with reservations.
2. Agile Methodology
Originally, the Agile project management methodology was designed in 2001 by 13 industry leaders as part of the Agile Manifesto for software development. Since then, agile methodology has also proven itself as a project management framework. Agile project management questions the processes, tasks, and role distributions of traditional approaches and replaces them with a more flexible, future-oriented principle. The optimization of customer benefit is foregrounded.
The core principle of the agile methodology is based on 12 guidelines and includes the following pillars:
- Direct and Open Communication
Agile project management methodologies are based on short, direct communication channels. When all team members are on the same level of knowledge, requests for changes can be responded to immediately and comprehensively.
- Implementation Cycles that Allow for Short-Term Changes
To optimize customer benefit, it must be possible to respond to short-term requests for changes. Instead of delivering a complete final package to the customer, which they may not be satisfied with, agile project management allows for regular feedback processes and constant improvement of the product – even during the project process!
- Implementation of Flat Hierarchies
Agile work can only be carried out in a familiar team atmosphere. Strict hierarchy prevents quick and flexible responses to requests for changes. In agile teams, each member acts on their own responsibility. Agile leaders must therefore be able to delegate tasks and responsibility and have trust in their employees.

What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
Agile project management methodologies are flexible in their application. Therefore, they are excellently suited for large, complex projects whose requirements are unpredictable and which can entail high risks. Aligned with the principles of the Agile Manifesto, various agile implementation methods, such as Scrum and Kanban, have been developed. However, since these have also developed their own structures, roles, and terminologies, they are treated as distinct project management methods in the following. Another project management tool that is especially popular in agile project management are Mind Maps. They help organize complex information and promote creativity and collaboration within the team.
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| Flexibility and Adaptability | Challenges in Scaling |
| Customer Focus and Feedback Integration | Lack of Predictability and Planning |
| Improved Team Dynamics and Communication | Excessive Dependence on Team Dynamics |
Unknown Fact: According to a survey by the PMI (Project Management Institute), agile projects have a higher success rate compared to traditional projects. The study found that 71% of agile projects were rated as successful compared to 55% of non-agile projects.
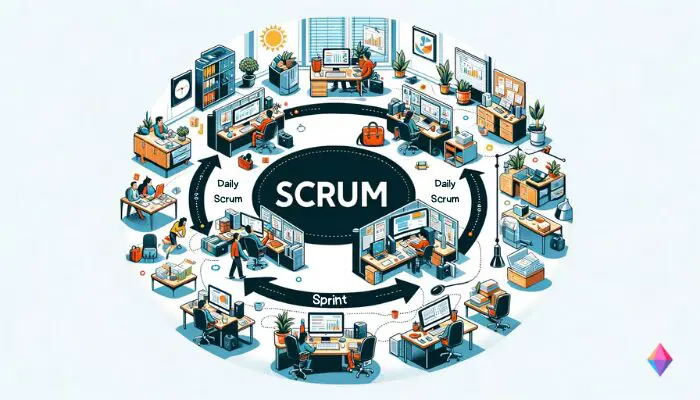
3. Scrum Methodology
Scrum is also considered an Agile method but distinguishes itself through its own set of firm rules, roles, and processes. This project management methodology is based on the notion that extensive projects are too complex to plan precisely in advance. Thus, most of the potential risks and requirements are unclear at the start of the project. To counter this fact, Scrum involves setting up and discussing interim results.
At the beginning of the project, Scrum establishes a long-term plan (Product Backlog). Unlike the traditional Waterfall methodology, this plan is regularly adjusted and optimized during the execution of the project. Tasks and actions associated with the project are implemented in repeating cycles (Sprints). Each Sprint aims to present a functioning interim product.
To enable Scrum teams to achieve this, all project participants gather at the start of each day in Daily Scrums to discuss tasks, problems, and progress. The Scrum project management methodology defines the following roles within a team:
- Product Owner: A product expert who represents the project’s stakeholders and advocates the views and wishes of the customer
- Development Team: A project team (e.g., developers and designers) that is involved in the execution of the project and takes on tasks
- Scrum Master: Facilitates and supports the development team and is responsible for ensuring that Scrum is correctly implemented. He also mediates between the development team and the Product Owner. However, it’s important to note that the Scrum Master does not play a traditional boss role. He does not dictate who should complete which task

What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
Scrum supports extensive, complex projects whose character is difficult to define in advance and therefore require a flexible project management methodology. Especially teams consisting of fewer than seven people benefit from Scrum.
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| Improved Flexibility and Responsiveness | Challenges in Scaling |
| Increased Team Collaboration and Communication | Dependence on Team Members and Their Commitment |
| Iterative Delivery of Product Increments | Risk of Incomplete Requirements |
Unknown Fact: Although Scrum originally emerged as a framework for software development, it was later successfully expanded to other industries, including marketing, HR, and even in the field of education.
4. Kanban Methodology
Kanban is based on regular feedback loops and teams that work independently. This Agile project management methodology was originally developed in the 1950s by Toyota in Japan. Kanban aims to optimally control each stage of a project to achieve faster throughput times.
The core principle of Kanban is effective teamwork. Short, daily stand-up meetings are practical, where all team members can discuss progress, successes, problems, and the next steps in the project.
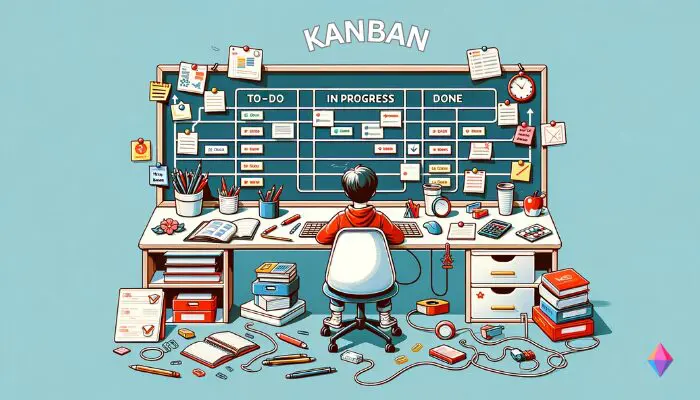
The Kanban method visualizes project workflows using Kanban boards. Kanban boards can be created both physically and digitally.
In the classic model, tasks that are not yet being processed are listed as To-Dos in the left column of the board.
When you start working on a task, move it to the middle column of the board and mark it as Doing. The Kanban method allows all team members to decide in which order to process tasks.
Once a task is considered complete, it is moved to the right column of the Kanban board and marked as Done.
It’s important to work on only a limited number of tasks simultaneously. A key aspect of implementing Kanban in project management is that tasks are consistently prioritized to keep processes clear and organized.
If a so-called bottleneck, or task backlog, forms, your Kanban board will show a large number of Kanban cards in the To-Do or Doing column. Here you must intervene and analyze the problem.
What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
Originally, Kanban was developed by Toyota for production and later adapted for software development by David Anderson in 2007. Nowadays, due to its transparent structures and high flexibility, Kanban can be used for any project that benefits from continuous improvements and feedback processes during its execution.
By the way: The Kanban project management methodology is perfect for personal and creative endeavours.
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| Visualization of Workflow | Risk of Overload |
| Flexibility in Task Management | Lack of Effectiveness in Complex Projects |
| Improvement of Team Collaboration | Lack of Long-Term Planning |
Unknown Fact: According to an internal analysis of companies that have implemented Kanban, the average cycle time for tasks has been reduced by up to 50%.
5. Lean Methodology
Lean aims to create value without waste. Customer benefit and process efficiency are optimized without wasting resources. The Lean project management methodology distinguishes between three different types of resource waste:
Muda
Muda refers to activities or processes that do not create value. Lean identifies potential resource wastage in seven original processes:
- Transport
- Inventory
- Movement (of employees)
- Waiting times
- Overproduction
- Incorrect use of technology or poor manufacturing processes
- Waste and possibly rework
Mura
Mura refers to losses that occur due to unbalanced processes. If the individual process steps are not aligned, deviations, irregularities, and disruptions arise.
Muri
Muri refers to an unbalanced workload on employees and machines. According to Lean principles, processes should neither be too fast nor too slow. Ideally, Lean reduces monotonous activities without overburdening employees and overloading machines.

What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
Since Lean (Project) Management is much more a project management philosophy than just a tool, this project management methodology is suitable for any company interested in transforming the values of their project management to save costs and other resources in the long term.
Key prerequisites for a comprehensive implementation of Lean project management are:
- Breaking up traditional thought structures and work processes
- The ability to design projects and processes flexibly
- A strong team culture
- Support from the entire leadership level
- A firm commitment to the company value of “customer proximity”
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| Increase in Efficiency | Overemphasis on Efficiency |
| Improved Customer Value Orientation | Challenges in Cultural Change |
| Promotion of Continuous Improvement | Potential Neglect of Employee Needs |
Unknown Fact: Lean project management is based on the principles of Kaizen, which means “continuous improvement” in Japanese. The constant pursuit of improvement at all levels of the company, from processes to work culture, contributes to strengthening the agility and adaptability of the organization.
10 popular project management methodologies, but only one home needed for all of them. Get the most out of your project
6. Six Sigma Methodology
The Six Sigma methodology was developed in 1987 in the USA by Motorola. Six Sigma is based on the assumption that every business process can be represented as a mathematical function. The description, measurement, analysis, control, and optimization of these processes are carried out using statistical means.
The main tool of this project management methodology is the DMAIC cycle. DMAIC aims to make business processes measurable and optimize them. The following actions determine the DMAIC cycle:
- Define: Identification and documentation of the problem in the process to be improved. What should the target state look like?
- Measure: To what extent does the process meet the requirements?
- Analyze: Identification of the causes of the problem
- Improve: Resolution of the problem
- Control: Ensuring the sustainability of the solution by monitoring the new process with statistical methods
The leadership of Six Sigma projects is undertaken by specially trained employees. The role designations in Six Sigma teams are based on the belt colors in Japanese martial arts, which serve as a ranking system. For example, there is the Master Black Belt (coach and trainer) or the Black Belt (project manager). A comprehensive explanation of all team roles in this project management methodology can be found here.

What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
Six Sigma is especially popular in large companies. This project management methodology is favored in the manufacturing industry and the service sector. Variants of the Six Sigma method have also become established in software development and the financial industry. Six Sigma is ideally suited for projects with clearly measurable results and a duration of between three and six months.
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| Quality Improvement and Error Reduction | High Training and Implementation Effort |
| Increase in Process Efficiency | Potential Overemphasis on Measurability |
| Structured Data Analysis and Decision Making | Resistance to Change |
Unknown Fact: The term “Six Sigma” refers to the statistical expression for a process’s ability to produce only 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
7. Critical Chain Project Management Methodology
Critical Chain project management (CCPM) is an effective project management methodology for managing projects based on the principles of the Theory of Constraints.
Unlike traditional project management approaches, CCPM focuses on the identification and management of bottlenecks in the project. The method concentrates on utilizing critical resources as effectively as possible to shorten throughput times.
The central idea behind CCPM is the creation of a critical chain of tasks, where buffer times are strategically used to account for uncertainties and fluctuations in the project’s progression.

What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
CCPM is particularly suitable for projects with uncertain resource capacities and dynamic requirements. This includes companies from various sectors such as manufacturing, IT, construction, research, and development. The method emphasizes the prioritization of tasks and maximizing efficiency, leading to accelerated project execution. Companies that value lean and targeted project management will find CCPM a valuable method for optimal project results.
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| Focus on Resource Optimization | Complexity in Implementation |
| Reduction of Project Duration and Costs | Potential Conflicts with Existing Processes |
| Increase in Project Reliability | Resistance to Change |
Unknown Fact: Critical Chain project management (CCPM) aims not only to identify bottlenecks but also to overcome psychological barriers. CCPM acknowledges that human uncertainty and behavior patterns can impact project performance. Therefore, the project management methodology integrates strategies to cope with uncertainty and promote a positive team environment.
8. PRINCE2 Methodology
Prince2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a proven project management methodology for structured project management that is recognized worldwide.
The method is characterized by clear processes, roles, and responsibilities. Prince2 defines detailed phases in the project cycle, starting with initiation, followed by planning, execution, control, and completion. It places great importance on the involvement of stakeholders and emphasizes the regular review and adjustment of the project status.

What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
Prince2 is particularly suitable for projects with clear definitions, fixed structures, and comprehensive documentation requirements. The method offers flexibility to adapt to various project sizes and types. Large companies with complex projects that seek a methodical approach with clear governance structures will find Prince2 to be a robust method for ensuring project success.
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| Structured and Standardized Method | Complexity and Learning Effort |
| Flexibility and Adaptability | Costs for Training and Certification |
| Risk Management | Potential Bureaucracy and Inflexibility |
Unknown Fact: Prince2, with its roots in IT projects, was originally developed in the United Kingdom and introduced by the British government.
9. Extreme Programming Methodology
Extreme Programming (XP) is an Agile methodology that focuses on software development and is based on principles such as flexibility and continuous improvement.
Originally developed in 1996, XP has evolved into a versatile project management methodology. XP emphasizes direct communication, collaboration, and customer orientation. With a focus on short development cycles (iterations), Extreme Programming enables rapid adaptation to changing requirements. Pair programming, Test Driven Development (TDD), and continuous integration are key elements of XP. These methods promote high code quality and early detection of errors.

What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
XP is particularly suitable for projects where the requirements are not clearly defined from the beginning and high flexibility is required. Companies looking for an Agile method to quickly respond to customer feedback and deliver high-quality software will find an effective solution in Extreme Programming (XP).
Opportunities & Risks
| Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|
| High Adaptability | Challenges in Scaling |
| Improvement of Software Quality | Increased Effort for Continuous Customer Involvement |
| Promotion of Team Collaboration | Potential Neglect of Planning and Documentation |
Unknown Fact: Extreme Programming popularized the practice of “User Stories”. User Stories are short, understandable descriptions of features or requirements from the perspective of the end-user. This method helps to improve usability and ensures that the developed features provide clear added value for the users.
10. PMI/PMBOK
PMI stands for the project management Institute which is a not-for-profit membership association, project management certification, and standards organization. Through the PMI, comes the PMBOK which is not quite a methodology but a guide detailing a set of standards that characterize project management.
PMBOK stands for the project management Body of Knowledge and is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. It states that there are five process groups that are prevalent in almost every project. They are:
- Initiating: Defining the start of a new project or new phase of an existing project.
- Planning: Where the scope of the project, objectives, and how the objectives will be achieved.
- Executing: Actually doing the work defined in the project management plan.
- Monitoring and Controlling: When you need to track, review, and regulate the progress and performance.
- Closing: Concluding all activities across all Process Groups to formally close the project or phrase.
Along with this, it includes best practices, conventions, and techniques that are considered the industry standard. Regularly updating their guide to ensure that they echo the most up-to-date project management practices, the PMBOK is currently up to its seventh edition which was published in print and online in 2021.
What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
Because it’s more of a reference guide than an actual project management methodology, you can’t implement PMI/PMBOK to a project. However, it can be used when you want to weigh in on the best practices for your project.
Unknown Fact: The PMBOK originated from an effort to standardize the information and practices in the field of project management and was first published as a white paper in 1987.
Have you found your Favorite?
Whether it’s a start-up, a corporation, a family business, or even for private projects – the presented selection of various project management methodologies includes solutions for (almost) every team size and project character.
If you have set your sights on one of the project management frameworks, you should familiarize yourself with it thoroughly once again. Especially complex project management methodologies like Scrum or Six Sigma fill entire books and must therefore be understood in the smallest detail.
Are you missing a specific methodology in our overview or would you like to learn more about one of the methods presented? Then leave us a comment. Have you successfully implemented one of the methods? Tell us and other readers about your experiences.
As always, we look forward to hearing from you.
See you soon!
FREE 20 MIN. CONSULTATION WITH A PROJECT MANAGEMENT EXPERT
Wanna see how to simplify your workflow with Zenkit in less than a day?
Book a Live Demo
Projects that require flexibility and have a level of complexity or uncertainty. For instance, a product or service that hasn’t been built by the team.
Agile is a methodology that has methodologies within itself, such as Scrum and Kanban. While some may argue that they should be considered more as frameworks, they are used to develop and deliver a product or service and carry their own set of characteristics and terminology which I think makes them worthy enough to be included on this list.
Hello,
What applications are best and worst suited for the use of Agile principles?
What are the challenges in using this approach that Systems Analysts and Project Managers need to be aware of?
What about research projects in Information technologies? What is the typical approach or does it very much depend on the type of domain of research?
Thanks
Hi Fernando,
The approach really depends on the type of domain of research. But I’ve found that agile approaches are common.
Thank you for sharing.
Brilliant overview or Synopsis. There is so much changing in project management world that it does get confusing. This article does align all ducks in a row.
Thanks, Yogesh. Appreciate your support!
Hi Donnie,
Hope this message finds you doing well!
I’m an aircraft engineer and currently interested I’m learning and being certified in QM systems. Now there is a lot of information available online on different methodologies being used hence too much information is not helping. I am currently working in the manufacturing industry where all sorts of vehicles are made.
So far I understand that the methodologies that will suit my industry would be six sigma, Kaizen and LEAN; please do correct me if I am wrong or if there are others available which I have not mentioned. Now with that said. I have 2 questions.
1. Which certification recommendations do you have for engineers in the manufacturing industry.
2. What methodology do you recommend for a startup manufacturing business and which methodologies should they evolve to.
Thank you so much for your time.
Regards,
Danish
Hi Danish,
Regarding certification, I would recommend enquiring with someone within the manufacturing industry as they’d have more knowledge about this kind of stuff. As for methodology recommendations, as you mentioned, LEAN and Six Sigma could work, but once again, I would advise doing further research.
what methodology is best suited for hospital management?
Hi Kiran,
Like most projects, it all depends. There are instances where Waterfall would be ideal, but then there are other instances where agile methodologies would best suit. I would recommend doing research beyond this article as we’re not too acquainted with hospital management. 🙂
Hi,
Could you please upload all of these as well ? ITIL, PYMBOK, PMI, Prince2. Lean, Waterfall, Six Sigma (I know some of them are mentioned and some of them are not)
PLEASE KINDLY UPLOAD THEM SOON !!!!
ESPECIALLY PRINCE 2 !!!!!!!
Hi Mitz, thanks for your suggestion. I’ll be sure to add it to our list.
If you have further feedback, I’d recommend sending them to our customer service team at service@zenkit.com 🙂
Is there a number I can reach you at. I am a general contractor submitting a bid on a large project and I need to provide an awful lot of information on project methodology. I would really appreciate if I could reach out to you for a quick call.
Hi Paul,
The best thing to do would be to send a quick email to sales@zenkit.com – our team will be able to get back to you and set up a time to call.
Hello Dinnie,
I am from finance field. But for my project book i need information of agile methodology. As i’m Non – IT background your article helps me to undestand it in a simple way & info which is in your article helps me to write it on my project book. Thank You..!!
Glad you’ve found the article helpful. Appreciate your support, Aditi.
What methodology would you recommend for a corporate email implementation? The current system needs updating to accommodate over 2,500 staff members.
Thank you for the concise explanation. I am currently in R&D and moving towards software development. I was not familiar with any software development methodologies before. Your article was very concise to get to know some of the well-known methodologies.
Thanks, Ali. Glad you found the article helpful 🙂
ITIL, PYMBOK, PMI, Prince2. Lean, Waterfall, Six Sigma are solid methods, structures or libraries used in conjunction.
Most of the other methodologies were invented due to the high cost of software development. Agile is really done in non regulated areas due to the high cost of documentation vs development so you find a great deal of in fighting in IT environments and then there are high rates of sacking until you find a team that works well in agile, scrum, kanban together. These methods are more a process requirements to me having studied most of the methods.
I am an IT specialist and I can tell you that any construction industry laughs at agile, scrum and kanban. Only suitable for IT and it creates bullying and discrimination. If you enforce ITIL then much of agile, kanban and scrum can be heaped into one name and that would be ‘continuous objectives’ which is not a project as the definition is one of a kind. The same type of software can be built numerous different ways and therefore fails the once off unique definition.
Great insight, Daffy. Thanks for sharing.
Pmi pmbok is not a methodology. P.2, 6 edt.
Hi,
I did point out that they’re not methodologies but more guides that detail a set of standards that characterize project management. Appreciate your comment. 🙂
Thanks for the article. It is easy to understand!
Glad you enjoyed it, Christelle 🙂
methodologies outlined clearly. Helpful. thanks
Appreciate your comment, Nancy. 🙂
Hi Dinnie,
first of all; I would like to thank you for the amazing article. secondly; If I have a design project (architectural) do you think that the best methodology for that is the Aigle?
Thanks
Hi Samar,
Glad you enjoyed the article 🙂 Agile isn’t the most popular method to use for design projects, however, if you feel that it could work for yours, it wouldn’t hurt to give it a go.
Hii good afternoon……Nice Info……Which company use agile method for quality assurance in software development?
Hi Nithya,
I’m sure many companies use agile methods for quality assurance in software development. Unfortunately, I couldn’t tell you which exactly. Thanks for reading 🙂
Hi Good afternoon. could you suggest the best methodology for a project in putting up IT infrastructure (Hardware setup).
Hi Jay 🙂
Considering a hardware setup is a pretty standard procedure, I would recommend something along the lines of the Waterfall method. There’s a lot of planning and documentation involved, so it could be fitting. Hope that helps!
Nice Info! Let me ask: and what about “CRISP-DM” methodology for Data Mining Projects? You think is a good option for? Regards from Perú!
Hi Juanalfieri,
I can’t say I’m overly experienced with CRISP-DM, so I would recommend further reading elsewhere. Thanks for the note though, I will look this up and perhaps include it in a revised version of this article 🙂
Thanks for the article. It amazing how it articulates so much knowledge, on a succinct way and gives to the user a quick and sufficient overview of the PM methods as well as the initial boost for a further research deepening down, if needed. What do you would be the best mix methods or mix of them in an ERP implementation such as SAP? Thanks in advance for your reply!
Thanks, Yannis!
I haven’t had any experience with ERP implementation myself, however, as they’re usually complex projects, perhaps something agile would be ideal. This is the part where I would suggest to do further research 🙂
Good overview in a prescise manner, easily understood…
Thanks Nazima 🙂
Thanks for the article, it was very helpful.
Cheers!
hye, what is the best methdology for gym management system? thank u
While I’m not all too familiar with gym management systems, I can recommend Kanban. It provides great flow management and the board and cards used offer a visual structure to track various tasks/items in the one place.
Hi Dinnie, great article and very informative. I currently work in a company and we execute contract both government and private contract. I was hired in February and there were 41 contract job being worked on. Ranging from road construction to procurement/supplies etc. I am having a hard time determining which methodology to use and how to track these projects. Most of them have been completed.
Hi Chris,
Construction and procurement are traditionally associated with Waterfall, however, I would advise to do further research on whether or not this would apply to your situation. Thanks for the support 🙂
What about Dev Ops methodology?
Can you check explain it .
Thanks .
Thanks for the tip, Abdulrahman.
Sounds like something that could be included in a revised version of this article.
What methodologies best suit in establishing a retail shop?
Hi Aruni,
Establishing a retail shop seems to me something that may involve a few uncertainties and surprises, so I would probably recommend something Agile as they provide leeway and flexibility.
excellent article. found it very useful. Thanks a lot
Cheers Abdul. Glad it could help 🙂
Good article, very informative and helpful.
Good job @Dinnie.
Thanks, Prativa 🙂
What about PRINCE2? It seems to me that PMI and PRINCE2 are quite comperable, but PMI is more common in US, while PRINCE2 in in EMEA region.
Very good overview btw, great work. 🙂
Thanks, Ivan 🙂
Ah yes, PRINCE2, perhaps I’ll have to include it in a revised version of this article. Cheers for the tip!